Flux - The rate of continuous change, flow or movement of liquid, particles or energy. The rate of discharge of a liquid, removal of energy or particle depositing from one body to another.
[Journal of Alloys and Compounds; v195; 407; 1993.]
[Ecological Monographs; v58; 177; 1988.]
Atmospheric Chemistry Glossary
The rate of flow of a physical quantitiy through a reference surface.
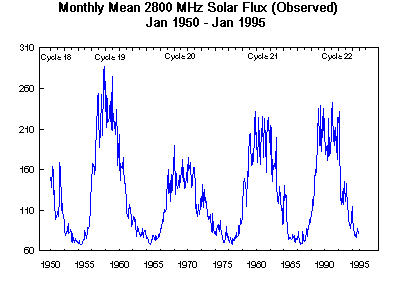
The sun emits radio energy with a slowly varying intensity. This radio flux, which originates from atmospheric layers high in the sun's chromosphere and low in its corona, changes gradually from day-to-day, in response to the number of spot groups on the disk. Radio intensity levels consist of emission from three sources: from the undisturbed solar surface, from developing active regions, and from short-lived enhancements above the daily level. Solar flux density at 2800 megaHertz has been recorded routinely by radio telescopes near Ottawa (February 14, 1947-May 31, 1991) and Penticton, British Columbia, since the first of June, 1991. Each day, levels are determined at local noon (1700 GMT at Ottawa and 2000 GMT at Penticton) and then corrected to within a few percent for factors such as antenna gain, atmospheric absorption, bursts in progress, and background sky temperature.
ON-LINE GLOSSARY OF SOLAR-TERRESTRIAL TERMS of National Geophysics Data Center |