Reflection is the process by which "a surface of discontinuity turns back a portion of the incident radiation into the medium through which the radiation approached." Reflection is important to take into account since about a third of the energy from the sun is reflected. If it was not for reflection, there would be a large portion of the world around us that we would not see. If an object does not emit its own light, it has to reflect it to be seen. The amount of energy reflected by the sun can be seen below in an image taken from the University of Oregon's Department of Geography's web page.
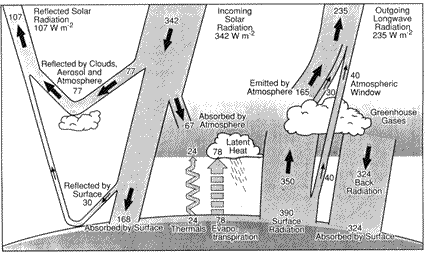
To have true reflection, a real discontinuity in the index of reflection is required. This discontinuity must be significant compared to the wavelength of the radiation, or the energy could be returned by way of refraction rather than reflection. An example would be in a stratified cloud deck where more refraction would take place than reflection.
The energy reflects off of a surface at the same angle at which it initially struck the surface, as seen below.
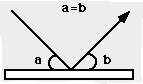
The incident light strikes the surface at an angle "a" and is reflected off of the surface at an angle "b." In this case of reflection, as stated above, angle a equals angle b. This is in accordance with Snell's Law, stating that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection.
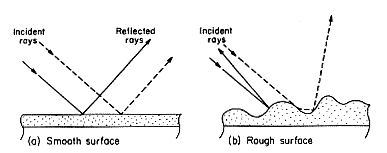
There are two types of reflection. There is specular reflection and diffuse reflection. Specular reflection, as seen in the left image from Arizona State University, shows a smooth surface where the light is reflecting off of it at equal angles from the plane perpendicular to the surface at the point of intersection. An example of diffuse reflection is the picture on the right. It continues to follow the rule of reflecting off of equal angles, but now the plane of reflection has changed.
An example of reflection can be seen in the sun pillar picture below, courtesy of the University of Illinois.

In this case, sunlight is reflected off of the tiny ice crystals creating the optical effects seen.
Atmospheric radiation, an online guide
The process whereby a surface turns back a portion of the radiation that strikes it.
WRCC Climate and Weather Terms Glossary
Although a radio wave is actually refracted in the ionosphere, it is often permissible to substitute a simple triangular ray path for the real ray path, as if the ray were reflected from a mirror. Thus radio waves are often referred to as being reflected from the ionosphere.
An Extended Glossary of Solar Terrestrial Terms from IPS Radio & Space Services The return of light or sound waves from a surface. If a reflecting surface is plane, the angle of reflection of a light ray is the same as the angle of incidence.
NASA Earth Observatory |